|
As of February 11, 2020,
there are 43,103 confirmed (2560 new) globally and in China with 42,708 confirmed (2484 new), 7,333 severe (849 new) and 1,017 deaths (108 new). Outside of China, the numbers are growing too with 395 confirmed (76 new) in 24 countries with 1 death.
Confirmed cases of 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease as of February 11, 2020
reported by provinces, regions and cities in China:
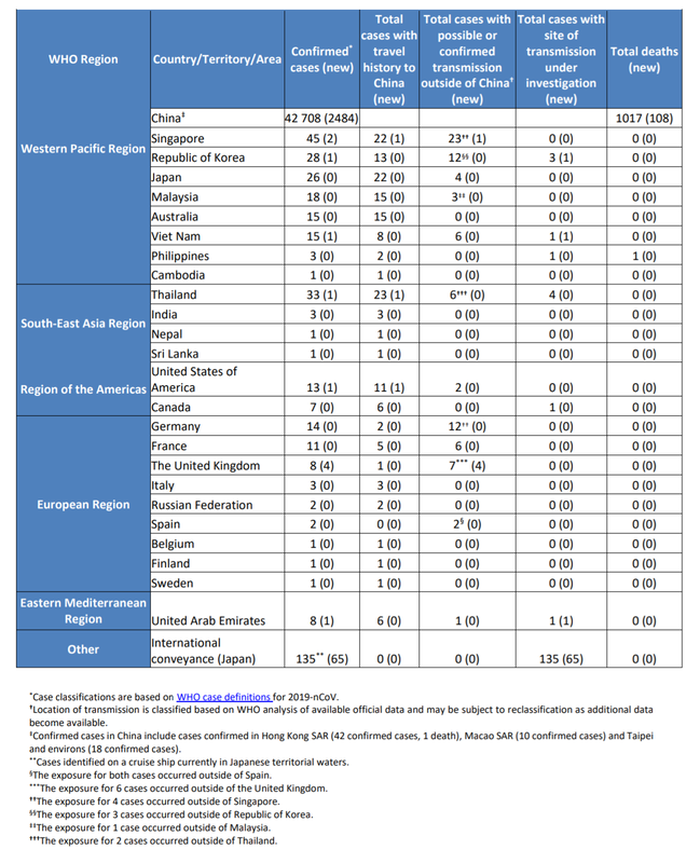
Countries, territories or areas with reported confirmed 2019-nCoV cases and deaths
as of February 11, 2020:
STRATEGIC OBJECTIVES
WHO’s strategic objectives for this response are to: • Limit human-to-human transmission including reducing secondary infections among close contacts and health care workers, preventing transmission amplification events, and preventing further international spread from China*; • Identify, isolate and care for patients early, including providing optimized care for infected patients; • Identify and reduce transmission from the animal source; • Address crucial unknowns regarding clinical severity, extent of transmission and infection, treatment options, and accelerate the development of diagnostics, therapeutics and vaccines; • Communicate critical risk and event information to all communities and counter misinformation; • Minimize social and economic impact through multisectoral partnerships. *This can be achieved through a combination of public health measures, such as rapid identification, diagnosis and management of the cases, identification and follow up of the contacts, infection prevention and control in health care settings, implementation of health measures for travelers, awareness-raising in the population and risk communication.
RECOMMENDATIONS AND ADVICE FOR THE PUBLIC
During previous outbreaks due to other coronavirus (Middle-East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), human-to-human transmission occurred through droplets, contact and fomites, suggesting that the transmission mode of the 2019-nCoV can be similar. The basic principles to reduce the general risk of transmission of acute respiratory infections include the following: • Avoiding close contact with people suffering from acute respiratory infections. • Frequent hand-washing, especially after direct contact with ill people or their environment. • Avoiding unprotected contact with farm or wild animals. • People with symptoms of acute respiratory infection should practice cough etiquette (maintain distance, cover coughs and sneezes with disposable tissues or clothing, and wash hands). • Within health care facilities, enhance standard infection prevention and control practices in hospitals, especially in emergency departments. WHO does not recommend any specific health measures for travellers. In case of symptoms suggestive of respiratory illness either during or after travel, travelers are encouraged to seek medical attention and share their travel history with their health care provider. SOURCE: WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Earth Blog
These are articles, stories and events that happen in this world that make impact on every nation and race.
Other Blogs
Archives
December 2023
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed